Liposomal technology represents a revolutionary approach to vitamin C delivery that addresses the fundamental limitations of conventional ascorbic acid supplementation. Vitamin C is essential for human health but faces significant bioavailability challenges due to saturable transport mechanisms and rapid elimination [3]. The bioavailability of vitamin C depends on limiting transport mechanisms that may be bypassed by liposome-encapsulation [3]. This comprehensive overview examines how liposomal encapsulation transforms vitamin C delivery, from basic mechanisms to clinical applications and future prospects.
What is Liposomal Technology and How Does It Work?
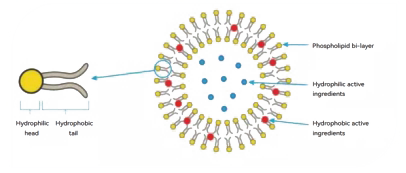
Liposomes are sphere-like vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers that can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances [19]. These lipid-based vesicles consist of biocompatible phospholipid membranes that form spherical structures with aqueous compartments [20]. The structural versatility of liposomes allows them to overcome challenges associated with conventional drug delivery systems [20].
Basic Structure and Composition of Liposomes
Mechanism of Action
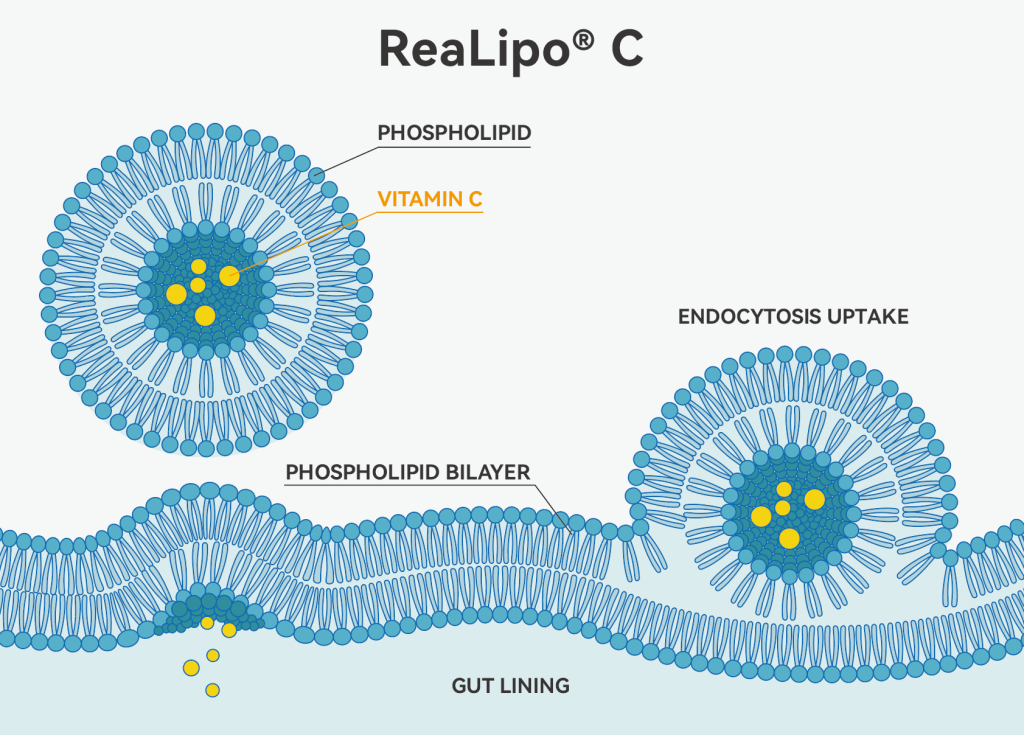
The fundamental mechanism involves encapsulating vitamin C within phospholipid vesicles that protect the nutrient from degradation and facilitate enhanced cellular uptake [4]. Liposomal systems work by:
- Protection from degradation: The phospholipid bilayer shields vitamin C from environmental factors and gastric conditions [5]
- Enhanced membrane fusion: Liposomes can fuse with cell membranes, facilitating direct intracellular delivery [3]
- Bypassing transport limitations: Unlike regular vitamin C which relies on saturable sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters (SVCT1 and SVCT2), liposomal vitamin C can enter cells through alternative pathways [3]
Advantages and Mechanisms of ReaLipo® C – Liposomal Vitamin C
1. Enhanced Stability and Protection
Liposomal encapsulation significantly improves vitamin C stability during storage and gastrointestinal transit [5]. The encapsulation process protects vitamin C from damage in gastrointestinal fluid and controls its release [5]. Studies demonstrate that liposomes can provide over 80% stability for vitamin C [13].
2. Superior Cellular Uptake
The phospholipid composition of liposomes facilitates enhanced cellular uptake through membrane fusion mechanisms [3]. This allows for more efficient delivery of vitamin C directly into cells, bypassing the limitations of traditional transport mechanisms [4].
3. Sustained Release Profile
Liposomal formulations provide controlled and sustained release of vitamin C, extending its therapeutic window [2]. The duration of elevated vitamin C blood levels is significantly longer with liposomal formulations [1].
Bioavailability and Absorption Differences
1. Pharmacokinetic Improvements
Clinical studies consistently demonstrate superior bioavailability of liposomal vitamin C compared to conventional forms:
- Area Under the Curve (AUC): Studies show 30% to 540% higher AUC values for liposomal vitamin C [1], [2], [14]
- Maximum Concentration (Cmax): Liposomal formulations achieve 1.2-5.4-fold higher peak plasma concentrations [14]
- Extended Half-life: Liposomal vitamin C demonstrates significantly longer plasma half-life [2]
2. Specific Bioavailability Data
A randomized, double-blind, cross-over trial found that liposomal vitamin C resulted in a 30% increase in AUC and 30% increase in 24-hour vitamin C levels compared to non-encapsulated vitamin C [1]. Another study reported vitamin C concentrations of 7.26±3.52 for liposomal process B vitamin C compared to 2.21±4.07 for vitamin C without liposome [2].
Clinical Evidence and Effectiveness of Liposomal Vitamin C
Randomized Controlled Trials
Multiple well-designed clinical studies support the efficacy of liposomal vitamin C:
- Cross-over Trial (n=10): Demonstrated 30% higher bioavailability with 1000mg liposomal vitamin C [1]
- Comparative Study (n=11): Showed superior absorption lasting up to 8 hours [2]
- Placebo-controlled Study (n=12): Found significantly higher blood levels at all timepoints compared to regular ascorbic acid [3]
Functional Benefits
Beyond bioavailability improvements, liposomal vitamin C demonstrates enhanced functional benefits:
- Antioxidant Capacity: Increased serum antioxidant capacity within 2 hours of consumption [3]
- Immune Function: Enhanced IFN-γ levels and anti-inflammatory effects [3]
- Ischemia-Reperfusion Protection: Provides protection similar to intravenous administration [8]
Manufacturing Processes and Formulation Considerations
Production Methods
Several manufacturing approaches have been developed for liposomal vitamin C:
- Solvent-free Methods: Advanced techniques avoid harmful organic solvents while maintaining liposome integrity [1], [4]
- High-Pressure Homogenization: Allows control over particle size and polydispersity, achieving >80% encapsulation efficiency [5]
- Spray Drying: Enables conversion of liquid liposomal suspensions to stable powder forms without affecting quality [1]
Quality Control Parameters
Key formulation considerations include:
- Particle Size: Controlled through pressure and cycle manipulation [5]
- Encapsulation Efficiency: Optimized formulations achieve >80% efficiency [5]
- Stability: Food-grade materials and proper processing ensure long-term stability [5]
Novel Approaches
Recent innovations include surface-modified natural fiber interlaced liposomal vitamin C systems that enhance stability and bioavailability [6]. These advanced formulations address challenges related to gastric stability and targeted release.
ReaLipo® C – Liposomal Vitamin C Applications
Liposomal vitamin C is currently used in:
- Nutritional Supplementation: Enhanced bioavailability for general health maintenance [1], [2]
- Therapeutic Applications: Higher-dose delivery for specific health conditions [8]
- Preventive Medicine: Antioxidant and immune support applications [3]
References :
Available upon request.